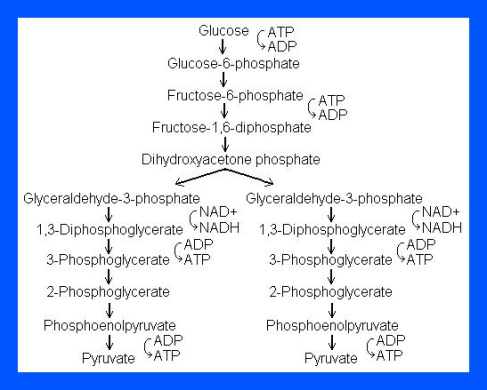
What is Glycolysis?
Glycolysis means the splitting of sugar. In glycolysis, glucose (a 6 carbon sugar) is split into 2 molecules of a 3-carbon sugar. Glycolysis yields 2 molecules of ATP (free energy containing molecule), 2 molecules of pyruvic acid & 2 “high energy” electron carrying molecules of NADH. Glycolysis can occur with (aerobically) or without oxygen (anaerobically). In the presence of oxygen, glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration. Without oxygen, glycolysis allows cells to make small amounts of ATP. This process is called fermentation.
The process of Glycolysis occurs through 10 steps.
Step 1
The enzyme hexokinase phosphorylates (adds a phosphate group to) glucose in the cell’s cytoplasm. In the process, a phosphate group from ATP is transferred to glucose producing glucose 6-phosphate.
- Glucose (C6H12O6) + hexokinase + ATP → ADP + Glucose 6-phosphate (C6H11O6P1)
Step 2
The enzyme phosphohexose isomerase converts glucose 6-phosphate into its isomer fructose 6-phosphate. Isomers have the same molecular formula, but the atoms of each molecule are arranged differently.
- Glucose 6-phosphate (C6H11O6P1) + Phosphoglucoisomerase → Fructose 6-phosphate (C6H11O6P1)
Step 3
The enzyme phosphofructokinase-1 uses another ATP molecule to transfer a phosphate group to fructose 6-phosphate to form fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate.
- Fructose 6-phosphate (C6H11O6P1) + phosphofructokinase + ATP → ADP + Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate (C6H10O6P2)
Step 4
The enzyme aldolase splits fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate into two sugars that are isomers of each other. These two sugars are dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde phosphate.
- Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate (C6H10O6P2) + aldolase → Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (C3H5O3P1) + Glyceraldehyde phosphate (C3H5O3P1)
Step 5
The enzyme triose phosphate isomerase rapidly inter-converts the molecules dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde phosphate. Glyceraldehyde phosphate is removed as soon as it is formed to be used in the next step of glycolysis.
- Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (C3H5O3P1) → Glyceraldehyde phosphate (C3H5O3P1)
Net result for steps 4 and 5: Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate (C6H10O6P2) ↔ 2 molecules of Glyceraldehyde phosphate (C3H5O3P1)
Step 6
The enzyme Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase serves two functions in this step. First the enzyme transfers a hydrogen (H–) from glyceraldehyde phosphate to the oxidizing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to form NADH. Next triose phosphate dehydrogenase adds a phosphate (P) from the cytosol to the oxidized glyceraldehyde phosphate to form 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate. This occurs for both molecules of glyceraldehyde phosphate produced in Step 5.
- Triose phosphate dehydrogenase + 2 H– + 2 NAD+ → 2 NADH + 2 H+
- Triose phosphate dehydrogenase + 2 P + 2 glyceraldehyde phosphate (C3H5O3P1) → 2 molecules of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (C3H4O4P2)
Step 7
The enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase transfers a P from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to a molecule of ADP to form ATP. This happens for each molecule of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. The process yields two 3-phosphoglycerate molecules and two ATP molecules.
- 2 molecules of 1,3-bisphoshoglycerate (C3H4O4P2) + phosphoglycerate kinase + 2 ADP → 2 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (C3H5O4P1) + 2 ATP
Step 8
The enzyme phosphoglycerate mutase relocates the P from 3-phosphoglycerate from the third carbon to the second carbon to form 2-phosphoglycerate.
- 2 molecules of 3-Phosphoglycerate (C3H5O4P1) + phosphoglyceromutase → 2 molecules of 2-Phosphoglycerate (C3H5O4P1)
Step 9
The enzyme enolase removes a molecule of water from 2-phosphoglycerate to form phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP). This happens for each molecule of 2-phosphoglycerate.
- 2 molecules of 2-Phosphoglycerate (C3H5O4P1) + enolase → 2 molecules of phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP) (C3H3O3P1)
Step 10
The enzyme pyruvate kinase transfers a P from PEP to ADP to form pyruvic acid and ATP. This happens for each molecule of PEP. This reaction yields 2 molecules of pyruvic acid and 2 ATP molecules.
- 2 molecules of PEP (C3H3O3P1) + pyruvate kinase + 2 ADP → 2 molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3) + 2 ATP
In summary, a single glucose molecule in glycolysis produces a total of 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, 2 molecules of ATP, 2 molecules of NADH and 2 molecules of water.
Although 2 ATP molecules are used in steps 1-3, 2 ATP molecules are generated in step 7 and 2 more in step 10. This gives a total of 4 ATP molecules produced. If you subtract the 2 ATP molecules used in steps 1-3 from the 4 generated at the end of step 10, you end up with a net total of 2 ATP molecules produced.